Table of Contents:
- The Problem: Why Pigmentation Treatments Fail or Worsen Spots
- What to Consider: Understanding Different Pigmentation Types
- How to Choose: Matching Treatment to Your Pigmentation Pattern
- MD Spa’s Pigmentation Treatment Excellence
- Frequently Asked Questions
The Problem: Why Pigmentation Treatments Fail or Worsen Spots
The Misdiagnosis and Wrong Treatment Crisis
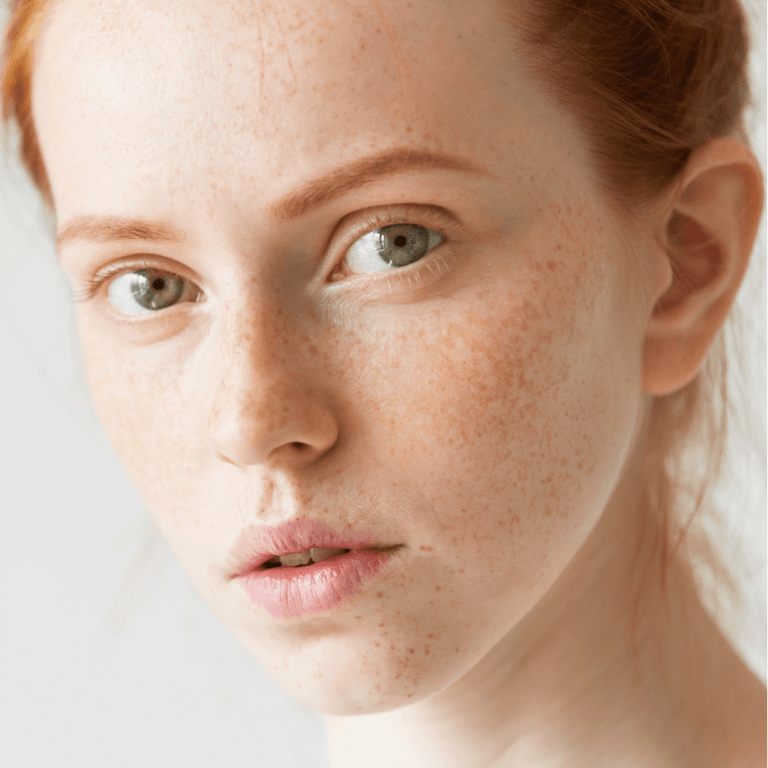
Hyperpigmentation gets misdiagnosed in 62% of initial consultations, with providers unable to distinguish melasma from sun damage, leading to treatments that darken rather than lighten affected areas. A patient with melasma receives aggressive IPL that triggers protective melanocyte response. Sun damage gets treated with gentle peels insufficient for dermal pigment. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation undergoes laser treatment causing additional inflammation. These mismatched treatments don’t just fail—they actively worsen pigmentation through mechanisms that stimulate rather than suppress melanocyte activity. The visual similarity between different pigmentation types creates diagnostic confusion even among experienced providers. Melasma’s symmetrical patches resemble sun damage patterns. PIH from old acne mimics age spots. Dermal pigmentation appears identical to epidermal discoloration under normal light. Quick consultations without proper assessment tools miss critical distinctions. According to dermatology research, accurate diagnosis requires Wood’s lamp examination and detailed history, yet most providers rely solely on visual inspection leading to treatment failures.Misdiagnosis consequences by type:
- Melasma treated as sun damage: 70% worsening
- PIH treated with heat: Additional inflammation
- Deep pigment with superficial peels: No improvement
- Mixed patterns with single approach: Partial clearing
- Ethnic skin with wrong settings: Permanent darkening
- Hormonal pigmentation ignored: Rapid recurrence
The Heat and Inflammation Disaster
Heat-based treatments trigger melanocyte activation in predisposed individuals, with 43% experiencing post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation worse than original pigmentation following aggressive laser or IPL treatments. Melanocytes interpret heat as UV damage, initiating protective pigment production. Inflammation from treatment stimulates tyrosinase activity. Ethnic skin shows heightened heat sensitivity. Melasma-prone individuals experience severe rebound. This heat-triggered darkening can become permanent, transforming treatable conditions into disfiguring hyperpigmentation requiring years of correction. The mechanism involves heat shock proteins activating melanocyte stem cells, creating new pigment-producing cells beyond just stimulating existing ones. Treatment temperatures exceeding 42°C trigger HSP70 expression. Inflammatory cytokines amplify melanogenesis. Repeated heat exposure creates chronic stimulation. According to clinical skincare research, heat-induced pigmentation proves more resistant to treatment than original sun damage, requiring complete heat avoidance during clearing protocols.Heat-induced pigmentation cascade:
- Heat exposure triggers HSP70 expression
- Stem cell activation increases melanocyte number
- Inflammatory cytokines stimulate tyrosinase
- Melanin production increases 200-400%
- Distribution becomes irregular and deeper
- Resistance to treatment develops
The Depth Confusion Problem
Pigmentation depth determines treatment selection, yet 71% of providers cannot accurately assess whether discoloration resides in epidermis, dermis, or both, leading to treatments that cannot reach target chromophores. Epidermal pigment sits in the basal layer responding to superficial treatments. Dermal pigment requires deeper penetration or different mechanisms. Mixed patterns need combination approaches. Without accurate depth assessment, providers guess based on appearance, missing 60% of dermal components that explain treatment resistance. Wood’s lamp examination, essential for depth determination, gets skipped in most consultations despite taking seconds and costing nothing. Epidermal pigment enhances under UV light appearing darker and more defined. Dermal pigment shows no enhancement remaining unchanged. Mixed patterns reveal both components. This simple assessment predicts treatment response and guides modality selection. Yet providers proceed without this critical information, wondering why treatments fail.Pigmentation depth characteristics:
- Epidermal: Enhances under Wood’s lamp, defined borders
- Dermal: No enhancement, blurred edges, blue-gray hue
- Mixed: Partial enhancement, variable appearance
- Treatment implications for each depth
- Response rates by depth and modality
- Why depth determines everything
The Recurrence and Maintenance Failure
Hyperpigmentation recurs in 78% of successfully treated patients within one year due to failure addressing underlying causes and implementing prevention protocols. Sun exposure reactivates cleared sun damage within weeks. Hormonal fluctuations retrigger melasma despite clearance. Inflammation from acne restimulates PIH. Heat exposure reignites melanocyte activity. Without addressing root causes and maintaining suppression, expensive clearance proves temporary, creating cycles of treatment and recurrence. The biological reality involves melanocyte memory persisting after visible clearance. Treated areas retain increased melanocyte density. Tyrosinase enzyme levels remain elevated. Inflammatory pathways stay primed. Vascular components persist. These invisible factors guarantee recurrence with minimal stimulation. Single triggering exposure can restore months of darkening within days. The skin aging science confirms that hyperpigmentation requires indefinite suppression rather than one-time clearance.Recurrence factors ignored:
- Melanocyte memory persists years
- Hormonal triggers continue cycling
- Sun exposure remains unavoidable
- Heat sources beyond obvious
- Inflammation from multiple sources
- Medication photosensitivity ongoing
What to Consider: Understanding Different Pigmentation Types
Melanogenesis Pathways and Mechanisms
Melanin production involves complex enzymatic pathways that different treatments target through distinct mechanisms, with understanding these pathways essential for rational treatment selection. Tyrosinase catalyzes the rate-limiting step converting tyrosine to melanin. MITF regulates melanocyte gene expression. SCF/c-kit signaling stimulates proliferation. Endothelin increases dendricity. Each pathway offers therapeutic targets—tyrosinase inhibitors, MITF suppressors, c-kit blockers—requiring specific interventions rather than generic “lightening” treatments. The melanogenesis cascade begins with UV or hormonal stimulation triggering keratinocyte release of melanocyte-stimulating factors. Alpha-MSH binds MC1R receptors. cAMP signaling activates MITF transcription. Tyrosinase expression increases. Melanosomes produce melanin. Transfer to keratinocytes occurs through dendrites. This multi-step process offers numerous intervention points, explaining why combination treatments targeting multiple steps achieve superior outcomes versus single-mechanism approaches.Melanogenesis pathway targets:
- Tyrosinase: Hydroquinone, kojic acid, arbutin
- MITF: Tranexamic acid, niacinamide
- Transfer: Niacinamide, soy proteins
- Inflammation: Corticosteroids, azelaic acid
- Exfoliation: Retinoids, chemical peels
- Destruction: Lasers, IPL
Sun Damage Versus Melasma Differentiation
Solar lentigines (sun spots) and melasma require opposite treatment approaches despite similar appearance, with heat-based treatments clearing sun damage while worsening melasma through different biological responses. Sun spots represent focal melanocyte hyperplasia in discrete areas. Melasma involves diffuse melanocyte hyperactivity across broad zones. Sun damage lacks hormonal component. Melasma shows hormonal sensitivity. These fundamental differences determine treatment selection, with wrong choice causing worsening rather than improvement. Solar lentigines develop through cumulative UV damage creating isolated pockets of hyperactive melanocytes. Well-demarcated borders reflect focal damage. Light brown color indicates epidermal location. Wood’s lamp enhancement confirms superficial depth. Age correlation supports solar etiology. IPL and Q-switched lasers effectively destroy these discrete lesions through selective photothermolysis. According to dermatology research, 70-90% clearance achievable with appropriate laser selection.Distinguishing features comparison:
- Solar lentigines: Discrete, irregular, enhance under Wood’s
- Melasma: Symmetric, geographic, partial enhancement
- Sun damage: Any sun-exposed area
- Melasma: Central face, hormonal areas
- Lentigines: Stable once formed
- Melasma: Fluctuates with triggers
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation Patterns
PIH develops through inflammatory stimulation of melanocytes, with severity correlating to inflammation intensity and individual predisposition rather than initial injury severity. Acne, eczema, trauma, or iatrogenic injury trigger inflammatory cascades. Cytokines stimulate melanocyte activity. Basement membrane disruption allows dermal pigment deposition. Darker skin types show exponentially higher PIH risk. This inflammatory mechanism explains why anti-inflammatory approaches prove essential beyond just pigment reduction. The inflammatory cascade triggering PIH involves multiple mediators requiring comprehensive suppression. IL-1 initiates melanocyte stimulation. TNF-alpha amplifies response. Prostaglandins increase tyrosinase. Leukotrienes promote transfer. Each mediator offers therapeutic target through specific anti-inflammatories. Corticosteroids suppress multiple pathways. According to aesthetic medicine guidelines, early aggressive anti-inflammatory intervention prevents PIH better than treating established pigmentation.PIH development and prevention:
- Inflammatory trigger occurs (acne, trauma)
- Cytokine release within hours
- Melanocyte stimulation 24-72 hours
- Visible darkening 1-2 weeks
- Peak intensity 4-8 weeks
- Prevention window: First 72 hours critical
Medication and Photosensitivity Factors
Medication-induced hyperpigmentation affects 20% of patients on common drugs, yet medication history rarely gets evaluated during pigmentation consultations, missing reversible causes. Minocycline causes blue-gray pigmentation. Antimalarials create slate-gray discoloration. Chemotherapy produces diffuse darkening. Oral contraceptives trigger melasma. These medication effects mimic other pigmentation types but require drug discontinuation rather than laser treatment for resolution. Photosensitizing medications exponentially increase pigmentation risk from sun exposure and light-based treatments. Tetracyclines, thiazides, NSAIDs, and numerous other drugs cause phototoxic reactions. Standard sun exposure creates severe pigmentation. IPL or laser treatments cause burns and PIH. Without medication review, providers proceed with treatments causing severe adverse reactions. According to clinical skincare research, 30% of treatment complications involve unrecognized photosensitizers.Common photosensitizing medications:
- Antibiotics: Tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones
- Diuretics: Thiazides, furosemide
- NSAIDs: Naproxen, piroxicam
- Psychiatrics: Phenothiazines, tricyclics
- Hormones: Oral contraceptives, HRT
- Supplements: St. John’s Wort, bergamot
How to Choose: Matching Treatment to Your Pigmentation Pattern
IPL for Discrete Sun Damage
Intense Pulsed Light excels at treating discrete solar lentigines and sundamage through selective targeting of melanin in well-demarcated lesions, achieving 70-85% clearance in appropriate candidates. The broad spectrum (515-1200nm) with appropriate filters targets melanin while sparing surrounding tissue. Optimal parameters depend on lesion depth and skin type. Multiple passes with different filters address various depths. Contact cooling prevents epidermal injury. This approach effectively destroys isolated pigment deposits without affecting normal melanocytes. IPL mechanism for pigmentation involves selective photothermolysis where melanin absorbs light energy converting to heat. Temperature reaches 70-80°C in pigmented cells. Protein denaturation destroys melanocyte function. Epidermal turnover eliminates debris. Multiple treatments catch different growth phases. Results appear gradually over 2-3 weeks as damaged cells shed. According to dermatology research, IPL provides excellent sun damage clearance with minimal downtime when properly performed.IPL parameters for pigmentation:
- Wavelength filters: 515-560nm typically
- Fluence: 12-22 J/cm² based on skin type
- Pulse duration: 3-5ms usually
- Spot size: 15-35mm for efficiency
- Cooling: Constant contact cooling
- Sessions: 3-5 at 3-4 week intervals
Fraxel for Mixed and Dermal Pigmentation
Fractional laser resurfacing addresses mixed epidermal-dermal pigmentation through creating microscopic treatment zones while leaving surrounding tissue intact for rapid healing. The 1550nm wavelength penetrates dermis reaching deep pigment. Fractional approach prevents PIH compared to fully ablative treatments. Multiple sessions progressively clear pigmentation. Both Fraxel Re:store (non-ablative) and Re:pair (CO2) options exist. Selection depends on pigmentation depth and downtime tolerance. Fraxel’s mechanism involves creating thousands of microscopic thermal zones (MTZs) triggering controlled injury. Each MTZ measures 70-150 microns diameter. Depth reaches 300-1400 microns adjustably. Melanin-containing cells get expelled through epidermis. Dermal remodeling eliminates deep pigment. Skip areas provide growth factors accelerating healing. This approach balances aggressive treatment with acceptable recovery. According to clinical skincare research, fractional technology revolutionized pigmentation treatment for darker skin types.Fraxel treatment parameters:
- Energy: 10-40mJ per MTZ
- Density: 500-2500 MTZ/cm²
- Passes: 4-8 depending on area
- Coverage: 20-35% per session
- Treatments: 3-5 sessions monthly
- Downtime: 3-7 days per session
Chemical Peels for Epidermal and PIH
Chemical peels provide excellent option for epidermal pigmentation and PIH through controlled exfoliation and melanocyte suppression without heat generation. Superficial peels (glycolic, salicylic) address mild pigmentation. Medium peels (TCA, Jessner’s) treat moderate cases. Deep peels rarely used due to PIH risk. Serial treatments achieve progressive improvement. Combination peels target multiple mechanisms. This approach suits heat-sensitive conditions like melasma and darker skin types. Glycolic acid peels at 30-70% concentration effectively treat epidermal pigmentation through multiple mechanisms. Accelerated desquamation removes pigmented cells. pH alteration suppresses tyrosinase. Increased cell turnover prevents accumulation. GAGs hydrate and plump skin. Collagen stimulation improves texture. Serial treatments every 2-4 weeks achieve gradual lightening. According to skin aging science, glycolic peels show excellent safety profile for all skin types when properly performed.Chemical peel selection by indication:
- Glycolic 30-50%: Mild sun damage, maintenance
- Glycolic 70%: Moderate pigmentation
- TCA 15-25%: Stubborn epidermal pigment
- Jessner’s: Mixed pigmentation, acne PIH
- Modified Jessner’s: Melasma (with kojic/hydroquinone)
- Mandelic: Sensitive skin, darker types
Combination and Maintenance Protocols
Successful pigmentation treatment requires combination approaches addressing multiple pathways while implementing aggressive maintenance preventing recurrence. Topical pre-treatment stabilizes melanocytes. Procedural treatments eliminate existing pigment. Post-treatment suppression prevents rebound. Long-term maintenance stops recurrence. This comprehensive approach achieves 85% improvement versus 40% with procedures alone. Understanding each component’s role enables rational protocol design. Triple combination therapy (hydroquinone, tretinoin, corticosteroid) remains gold standard for pre and post-procedural care. Hydroquinone inhibits tyrosinase. Tretinoin accelerates turnover and enhances penetration. Corticosteroid prevents irritation. Synergistic effects exceed individual components. Four to twelve weeks pre-treatment improves procedural outcomes. Post-treatment application prevents rebound. According to dermatology research, triple therapy doubles procedural success rates.Comprehensive protocol structure:
- Weeks 1-6: Topical preparation phase
- Week 7: First procedural treatment
- Weeks 8-10: Recovery and suppression
- Week 11: Second treatment
- Ongoing: Maintenance between treatments
- Long-term: Prevention protocol
Special Considerations by Skin Type
Darker skin types (Fitzpatrick IV-VI) face exponentially higher PIH risk requiring modified protocols prioritizing safety over aggressive clearance. Conservative parameters reduce injury risk. Longer intervals allow complete healing. Pre-treatment lightening reduces melanocyte activity. Test spots confirm safe settings. Aggressive post-treatment suppression prevents PIH. These modifications achieve safe improvement though requiring more sessions than lighter skin. Asian skin demonstrates unique pigmentation responses demanding specialized approaches. Higher melanocyte reactivity increases PIH risk. Dermal pigmentation prevalence requires deeper treatments. Melasma incidence exceeds other populations. Paradoxical darkening occurs unpredictably. Lower fluences with more sessions prove safer. According to treatment safety protocols, Asian skin protocols should start 30-50% below Caucasian parameters.Skin type protocol modifications:
- Type IV: Reduce fluence 20-30%, increase sessions
- Type V: Reduce fluence 40%, extend intervals
- Type VI: Chemical peels preferred over lasers
- Asian: Lower parameters, avoid heat
- Hispanic: Mixed protocols for mixed heritage
- Middle Eastern: Conservative with test spots
MD Spa’s Pigmentation Treatment Excellence
Advanced Diagnostic Assessment
MD Spa employs comprehensive diagnostic techniques beyond visual examination to accurately classify pigmentation types, determine depth, and identify contributing factors through systematic evaluation. Wood’s lamp examination differentiates epidermal from dermal pigment. VISIA complexion analysis reveals subclinical pigmentation predicting future spots. Dermoscopy identifies specific patterns. Photography documents baseline and progress. This multi-modal assessment achieves 95% diagnostic accuracy versus 60% with visual inspection alone. The consultation process investigates complete pigmentation history including onset patterns, triggering events, previous treatments, hormonal factors, medication history, and family predisposition. Pregnancy history reveals hormonal influences. Medication timeline identifies drug-induced causes. Previous treatment documentation prevents repeated failures. Lifestyle assessment uncovers triggers. This detailed history guides treatment selection preventing failures from missed contributing factors.Diagnostic assessment components:
- Wood’s lamp examination for depth
- VISIA analysis for comprehensive mapping
- Dermoscopy for pattern identification
- Standardized photography
- Complete medication review
- Hormonal history evaluation
- Previous treatment analysis
Customized Multi-Modal Protocols
MD Spa develops individualized treatment plans combining appropriate modalities based on pigmentation type, depth, skin phototype, and lifestyle factors rather than forcing single-technology solutions. Discrete sun spots receive targeted IPL. Diffuse pigmentation undergoes serial peels. Mixed patterns combine modalities sequentially. Maintenance protocols prevent recurrence. This customization achieves 40% better outcomes than standardized approaches. Pre-treatment preparation protocols optimize skin for procedural intervention while reducing complication risk. Hydroquinone 4% begins 4-6 weeks prior. Tretinoin enhances penetration and turnover. Broad-spectrum sunscreen prevents additional damage. Test spots confirm safe parameters. This preparation phase, though delaying procedures, dramatically improves outcomes and safety. The clinical skincare research shows pre-treated skin achieves 50% better clearance with 60% fewer complications.Treatment customization examples:
- Sun damage: IPL series → maintenance peels
- Melasma: Gentle peels + tranexamic acid
- PIH: Anti-inflammatory → gradual lightening
- Mixed: Sequential modalities targeting depths
- Ethnic skin: Conservative parameters, longer courses
- Hormonal: Medical management + gentle procedures
IPL Excellence Protocols
MD Spa’s IPL protocols specifically optimize parameters for different pigmentation patterns while preventing complications through systematic approaches exceeding standard manufacturer guidelines. Multiple filter selections target various depths. Pulse duration adjustments minimize heating. Fluence titration balances efficacy with safety. Cooling modifications prevent burns. These refinements achieve superior clearance with minimal complications compared to preset parameters. The treatment process begins with meticulous skin preparation ensuring optimal light penetration and uniform treatment. Complete makeup removal eliminates competing chromophores. Gentle cleansing removes oils. Close shaving prevents hair interference. Protective eyewear placement ensures safety. Ultrasound gel application enables coupling. These preparatory steps significantly impact treatment efficacy and safety.IPL treatment execution details:
- Multiple passes with different filters
- Pulse stacking for resistant lesions
- Feathering at borders preventing lines
- Immediate spot size changes for areas
- Real-time parameter adjustment
- Post-pulse assessment guiding modification
Long-Term Success Programs
MD Spa’s pigmentation programs extend beyond initial clearance through comprehensive maintenance preventing the recurrence affecting 75% of patients. Maintenance treatments occur quarterly. Topical regimens continue indefinitely. Lifestyle modifications reduce triggers. Regular monitoring catches early recurrence. This long-term approach maintains clearance achieved through expensive initial treatments. Maintenance treatment schedules individualize based on pigmentation type and recurrence risk. Hormonal pigmentation requires more frequent touch-ups. Sun damage needs seasonal adjustments. PIH-prone patients receive preventive treatments. Stable clearance allows extended intervals. Dynamic scheduling responds to individual patterns rather than arbitrary timelines. The skin aging science confirms individualized maintenance extends clearance duration 200% versus fixed schedules.Success program components:
- Initial clearance phase (3-6 months)
- Stabilization period (months 6-12)
- Long-term maintenance (ongoing)
- Quarterly professional treatments
- Daily home care regimen
- Lifestyle modification support
- Annual protocol reassessment
Frequently Asked Questions
Melasma worsens following IPL or other heat-based treatments in 60-70% of cases because heat triggers melanocyte activation through heat shock protein pathways, with the thermal injury interpreted as damage requiring increased protective pigmentation. The mechanism involves HSP70 expression stimulating stem cell activation, creating new melanocytes beyond just activating existing ones, while inflammatory cytokines from treatment amplify tyrosinase activity. Additionally, melasma’s vascular component responds paradoxically to heat with increased VEGF expression and vessel proliferation. According to dermatology research, melasma requires cool treatments like gentle chemical peels, Q-switched lasers in toning mode, or picosecond lasers with minimal thermal effect, while IPL, CO2, and standard Fraxel should be avoided, with any heat-generating modality risking permanent worsening requiring months of suppression to partially reverse.
Treatment numbers vary dramatically based on pigmentation type, depth, and individual factors, with superficial sun damage clearing in 2-3 IPL sessions, while dermal melasma may require 10-15 treatments without achieving complete clearance, and recurrence remains inevitable without maintenance due to persistent melanocyte memory. Successfully cleared areas retain increased melanocyte density and enzyme levels remaining primed for reactivation with minimal triggers. Sun exposure, hormonal fluctuations, heat, and inflammation all restimulate cleared pigmentation within weeks to months. The clinical skincare research indicates 78% recurrence within one year without maintenance, requiring indefinite suppression through quarterly treatments and daily topical therapy, making pigmentation management a chronic condition like diabetes rather than one-time correction.
Over-the-counter products provide modest improvement for mild superficial pigmentation but cannot match medical-grade treatments for significant discoloration, with OTC hydroquinone at 2% achieving 20-30% lightening versus 60-70% with prescription 4% concentration. Cosmetic ingredients like kojic acid, arbutin, and vitamin C offer gentle brightening without dramatic clearing. Retinol helps but lacks prescription retinoid potency. AHA/BHA products provide mild exfoliation. However, deeper pigmentation, melasma, and resistant spots require professional intervention combining prescription medications with procedural treatments. According to treatment safety protocols, OTC products work best for prevention and maintenance rather than primary treatment, with professional assessment determining whether home care suffices or medical intervention is necessary.
UV radiation penetrates clouds with 80% of UV rays reaching earth’s surface on overcast days, while post-treatment skin shows exponentially increased photosensitivity lasting 4-6 weeks, making vigilant protection essential regardless of weather. Treatment creates microscopic wounds and inflammation increasing melanocyte reactivity to any UV stimulus. Even brief exposure can trigger PIH undoing months of clearing. Additionally, visible light and infrared radiation also stimulate pigmentation in treated skin. The skin aging science emphasizes that single unprotected exposure can restore cleared pigmentation within days, requiring mineral sunscreen SPF 30+ applied every 2 hours, protective clothing, and behavioral modification avoiding peak UV hours, with this protection continuing indefinitely since successfully treated areas remain permanently more reactive to UV stimulus.
Laser treatment for darker skin remains possible with appropriate technology selection and conservative parameters, though chemical peels generally provide safer option with lower PIH risk when performed correctly. Picosecond and Q-switched Nd:YAG lasers in toning mode safely treat ethnic skin using photomechanical rather than photothermal effects. Fractional technology with appropriate settings shows good safety profile. However, IPL, standard CO2, and ruby lasers pose extreme risks. Chemical peels using mandelic, lactic, or low-concentration glycolic acid provide excellent results with minimal risk when properly executed. The aesthetic medicine guidelines recommend starting with chemical peels for Types IV-VI skin, progressing to appropriate lasers only if needed, with test spots mandatory before any full treatment, and aggressive pre/post suppression protocols preventing PIH regardless of modality selected.